Bitcoin, Ether, and other popular crypto-currencies are powered by blockchain technology and the latter has also become popular as it has found potential applications across various industries.
Let’s look into into this technology in a simplified way, how it works, potential applications, pros and cons of using this technology.
What is Blockchain Technology
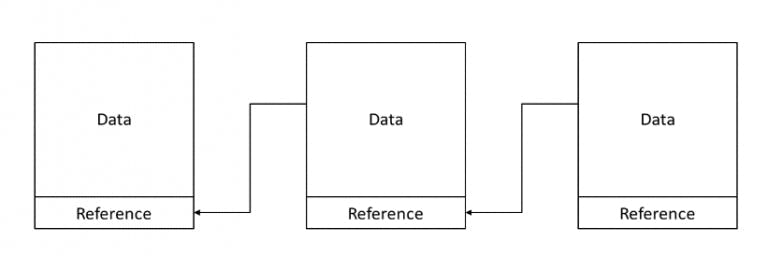
A blockchain is a growing list of data blocks that are linked together.
Blockchain technology is a structure that stores transactional records, also known as the block, of the public in several databases, known as the “chain,” in a network connected through peer-to-peer nodes.
Typically, this storage is referred to as a ‘digital ledger.’
It’s key features are:
- Write-only
- Immutable
- Transparent data storage
- Decentralized%20to%20a%20distributed%20network.)
- No need for intermediaries
- Consistent state across all participants
- Resistant against malicious participants
- Open to everyone
Blockchain is popular due to its:
- High Security
It uses a digital signature feature to conduct fraud-free transactions making it impossible to corrupt or change the data of an individual by the other users without a specific digital signature
- Decentralized System
Block chain, transactions are done with the mutual consensus of users resulting in smoother, safer, and faster transactions.
- Automation Capability
It is programmable and can generate systematic actions, events, and payments automatically when the criteria of the trigger are met.
Combination of Three Leading Technologies
Blockchain technology works mainly combination of three leading technologies:
- Cryptographic keys
Consists of two keys – private and public keys.
These keys help in performing successful transactions between two parties.
Each individual has these two keys, which they use to produce a secure digital identity reference. This identity is referred to as ‘digital signature’ and is used for authorizing and controlling transactions.
- A peer-to-peer network containing a shared ledger
The digital signature is merged with the [peer-to-peer network](webroot.com/in/en/resources/glossary/what-i...
- A means of computing
When they authorize a deal, it is certified by a mathematical verification, which results in a successful secured transaction between the two network-connected parties.
So to sum it up, Blockchain users employ cryptography keys to perform different types of digital interactions over the peer-to-peer network.
4 Different Types of Blockchain
- Private Blockchain Networks
They operate on closed networks, work well for private businesses and organizations.
Companies can use private blockchains to customize their accessibility and authorization preferences, parameters to the network, and other important security options. Only one authority manages a private blockchain network.
- Public Blockchain Networks
Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies originated from public blockchains, which also played a role in popularizing distributed ledger technology (DLT).
- Permissioned Blockchain Networks
They are known as hybrid blockchains, permissioned blockchain networks are private blockchains that allow special access for authorized individuals.
Organizations typically set up these types of blockchains to get the best of both worlds, and it enables better structure when assigning who can participate in the network and in what transactions.
- Consortium Blockchain Networks
They have both public and private components, except multiple organizations will manage a single consortium blockchain network.
Although these types of blockchains can initially be more complex to set up, once they are running, they can offer better security.
Additionally, consortium blockchains are optimal for collaboration with multiple organizations.
Process of Transactions Happening Inside a Blockchain Network
Blockchain technology’s important features is the way that it confirms and authorizes transactions.
For example, if two individuals wish to start a transaction with a private and public key, respectively, the first person would attach the transaction information to the public key of the second party.
This total information is collected as block.
The block contains a digital signature, a timestamp, and other important, relevant information. It should be noted that the block doesn’t include the identities of the individuals involved in the transaction.
This block is then transmitted across all of the network’s nodes, and when the right individual uses his private key and matches it with the block, the transaction gets completed successfully.
Hash Encryption in Blockchain
Majority of the blockchain networks use hashing and encryption to secure the data, relying mainly on the SHA256 algorithm to secure the information.
The address of the sender (public key), the receiver’s address, the transaction, and his/her private key details are transmitted via the SHA256 algorithm.
The encrypted information, called hash encryption, is transmitted across the world and added to the blockchain after verification.
The SHA256 algorithm makes it almost impossible to hack the hash encryption, which in turn simplifies the sender and receiver’s authentication.
Proof of Work
Blockchain, each block consists of 4 main headers.
- Previous Hash
This hash address locates the previous block.
- Transaction Details
Details of all the transactions that need to occur.
- Nonce
An arbitrary number given in cryptography to differentiate the block’s hash address.
- Hash Address of the Block
Preceding hash, transaction details, and nonce were transmitted through a hashing algorithm.
This gives an output containing a 256-bit, 64 character length value, which is called the unique ‘hash address.’ it is referred to as the hash of the block.
Many people around the world try to find out the correct hash value to meet a predetermined condition using computational algorithms, this transaction completes once this predetermined condition is met.
Blockchain miners attempt to solve a mathematical puzzle, which is referred to as a proof of work problem. Whoever solves it first gets a reward.
List of Potential Blockchain Technology Applications
- Cloud Storage
- Cryptocurrency
- Healthcare
- Smart Contracts
- Elections
- Digital Identity Management
- Intellectual Property Protection
Pros and Cons of Using Blockchain Technology
Pros:
- Immutable public digital ledger
- Security
- Speedy and convenient transactions
- No third-party interference from financial institutions or government organizations
- Underlying technology for cryptocurrencies
Cons:
- If a user loses their private key, they face numerous challenges
- Scalability restrictions
- Difficult to change or add information after it is recorded.
Final Thoughts
Hope this post has provided you a basic understanding of blockchain technology, how it works, it’s features, what’s happening inside a blockchain network, and potential applications.
If you have any suggestions or opinions, let us know about them in the comments.
If you have queries about developing an application powered by blockchain, feel free to get in touch with us.
